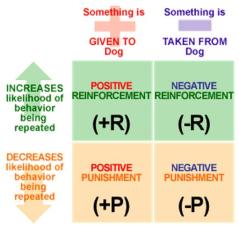
First described by US Psychologist Edward Thorndyke, Operant Conditioning focuses on voluntary behaviors. It is used to incrementally shape behavior by providing positive consequences for desired behaviors and negative consequences for undesired behaviors.
Effective punishment usually embodies the following qualities: it is consistent, immediate, impersonal, and contingent on specific behavior. Finally, punishment should be informative letting employees know why they are being punished employees should recognize that future punishment can be avoided by refraining from the undesired behavior.
Maximizing the effectiveness of punishment explains why researchers rely heavily on monitored communications within the past 24 hour or less to inflict psychological abuse. That the abuse focuses on immigration and race lets me know what it’s about. However, that there is no escape or avoidance of abuse never ends no matter what I say or do demonstrates that the ultimate goal of the harassment is to psychological torture.
For an overview of applied psychology see http://www.education.com/reference/article/applied-behavior-analysis/
|
‘Becoming legally blond’ Worksheet for Operant Conditioning and Coercive Psychology |
|||
|
Use this worksheet to analyze harassment events and illustrate their intent. https://saskiawhistleblower.wordpress.com/category/4-harassment-methods/psyops/ Also see flybybutterfly’s excellent videos on Classical Conditioning. |
|||
|
Goal |
Tactics |
Response |
|
| 1a | Positive reinforcement (R+): Reward: behavior | Researcher: present positives to increase ‘niceness’ (bonus, overtime, merits, perks, promotion). | Subject: increase ‘niceness’ to gain more high value awards (affirm everyone). |
| 1b | Coercive psychology (R+): Corrupt: reward desired behavior even if unethical or harmful | ||
| 1c | Coercive psychology (R+): Lure: encourage a behavior then penalize (frenemies) | ||
| 1c | Coercive psychology (R+): Sting: present an opportunity for unethical behavior then penalize or exploit | ||
| 2a | Positive punishment (P+): Penalize behavior | Researcher: present negatives to decrease ‘hostility’ (low value rewards, low status tasks, demotion, fines, loss of points). | Subject: decrease statements viewed as ‘hostile’ to reduce penalties (talk in euphemisms) |
| 2b | Coercive psychology (P+): Entrap: race bait to illicit hostile response then penalize as malicious harassment, etc. | ||
| 2c | Coercive psychology (P+): Frame: to contrive evidence to incriminate. | ||
| 2d | Coercive psychology (P+): Gas-lighting: stage incredulous events to discredit witnesses sanity | ||
| 3a | Negative reinforcement (R-): Avoid negative conditions | Researcher: increase ‘niceness’ by removing impending negative conditions. | Subject: increase ‘niceness’ to avoid impending social undermining (be a sycophant). |
| 3b | Coercive psychology (R-): No avoidance in the workplace of persecution or social undermining no matter how nice. | ||
| 3c | Coercive psychology (R-): No avoidance in the community of persecution or social undermining no matter how nice. | ||
| 3d | Coercive psychology (R-): No avoidance in behavioral sciences of persecution or social undermining no matter how nice. | ||
| 4a | Negative punishment (P-): Escape negative conditions | Researcher: reduce ‘hostility’ by removing an existing negative condition. | Subject: escape persecution by suppressing anger when race-baited to avoid anything you say being interpreted as ‘hostile’ (smile and take aspirin to protect your heart). |
| 4b | Coercive psychology (P-): No escape in the workplacefrom persecution when silent on political issues inside the workplace | ||
| 4c | Coercive psychology (P-): No escape in the communityfrom persecution if fair and respectful when questioning, challenging or opposing political issues | ||
| 4d | Coercive psychology (P-): No escape in behavioral sciencesfrom persecution if fair and respectful when questioning, challenging or opposing political issues | ||
Videos
Documentary – BF Skinner – classroom
Operant Conditioning – 4 quadrants
BF Skinner – big dream
Example – teaching pigeons to read
Example – teaching pigeons ping-pong
Rescorla-Wagner Model – surprise elements for super learning
Example – toot toot
Related articles
- Week 11 (16 – 20 Jan): Operant Conditioning (ptzapblog.wordpress.com)
- Decimals Worksheets and Printables (education.com)
- Weeks 10 & 11 Blog Post Prompts (mrmzworld.wordpress.com)
- Operant Conditioning (cheerfulappsych.wordpress.com)
- Operant Conditioning (sunshineserenade.wordpress.com)
- Punctuation Worksheets and Printables (education.com)
- Operant Conditioning Chamber (socyberty.com)
- Class activity 11 12 march (slideshare.net)
- Word Families Worksheets and Printables (education.com)
- Fractions Worksheets and Printables (education.com)